What is Photo Transistor?
Photo Transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device which converts the incident light into photocurrent. Light is incident on the base terminal and it is converted into current which flows through emitter and collector. It is the combination of photo diode and transistor an amplifier. The current produced by the photo diode is low, so it is sent through the transistor and amplified.
Symbol of Photo Transistor:
The symbol of Photo Transistor is similar to the transistor. The arrows shows the light incident on the base terminal.
Construction of Photo Transistor:
 |
| Construction of Photo Transistor |
When compared to normal transistor, in photo transistor the base and collector area is large. The base area is increased to increase the amount of current generated. Because more the light falls more the current is generated. Earlier it was made up of single semiconductor material like silicon or germanium. Recently photo transistors are made up of Gallium and Arsenic to obtain higher efficiency. Finally photo transistor is placed inside a metallic case and a lens is kept at the top of the case to absorb the incident radiation.
Working of Photo Transistor:
From the above circuit we can know that base is not connected to any external bias and only light is incident on the base terminal. Collector terminal is connected to the positive side of external supply and output is taken from the emitter terminal.
When no light is incident on the base terminal only some leakage current flows and it is called as dark current. When light is incident on the lens at the base collector junction, base current is generated which is proportional to the intensity of the incident light.
Characteristics of Photo Transistor:
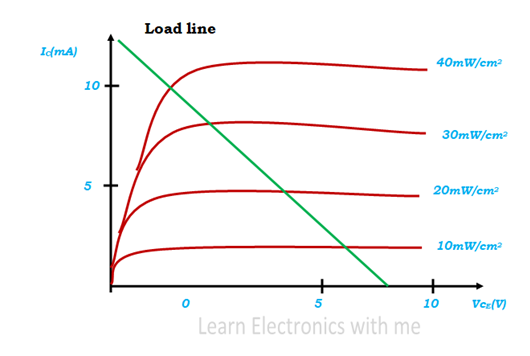 |
| Characteristics of Photo Transistor |
From the above figure we can observe how the collector current varies with the intensity of the incident light. The collector current increases with the intensity of the incident light. Collector current differs with the wavelength and the intensity of the light.
Advantages:
- Efficiency is high
- Faster response
- Less noise interference
- Low cost
- Small in size
Disadvantages:
- Poor performance at high frequency
- Slower than photodiode
Applications:
- Used in Counting systems
- Used in Optical tape reader
- Used to detect Object
- Used in printers




0 Comments